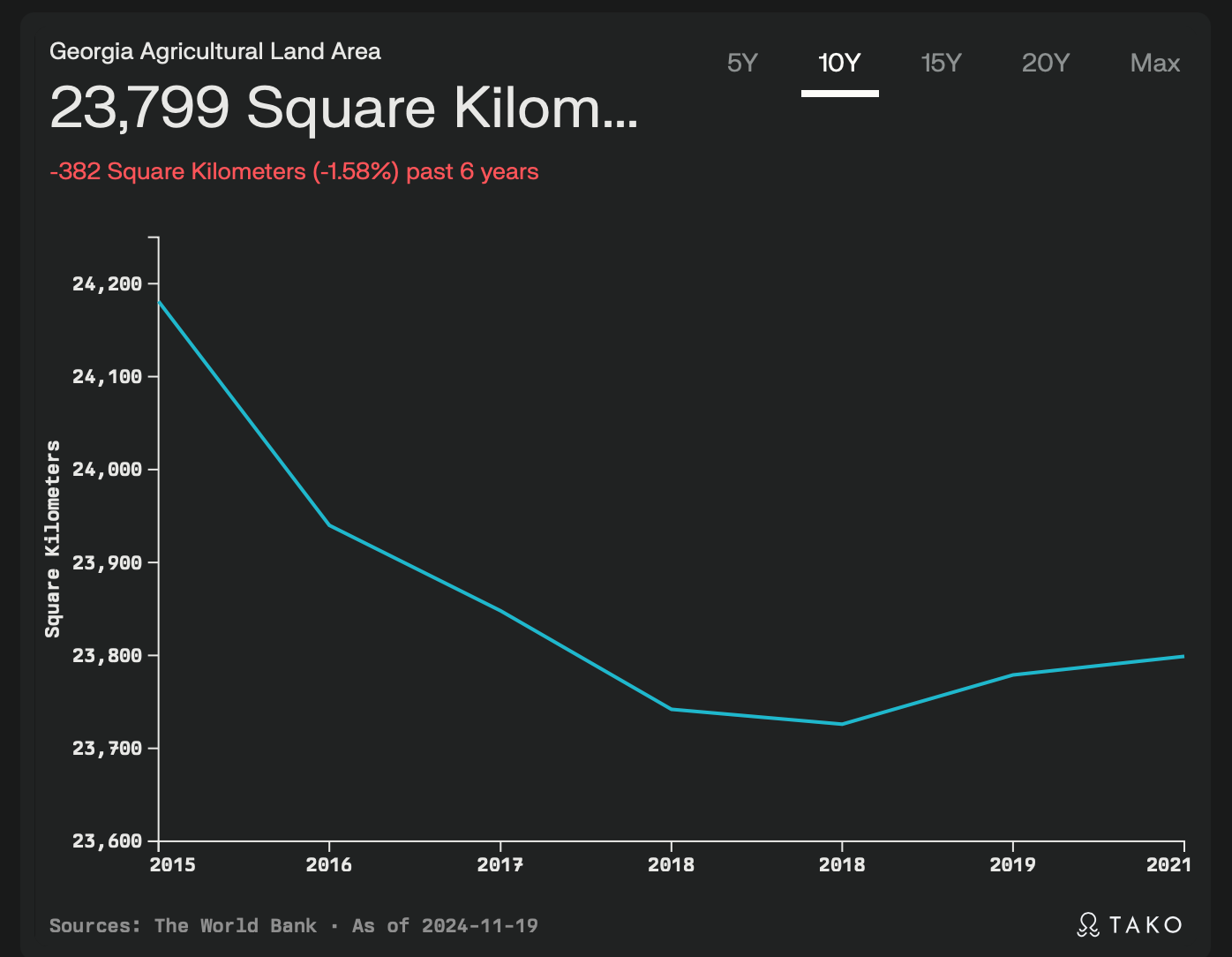
Agricultural Land Area in Georgia
The chart below shows the distribution of land area for different types of agriculture in Georgia.
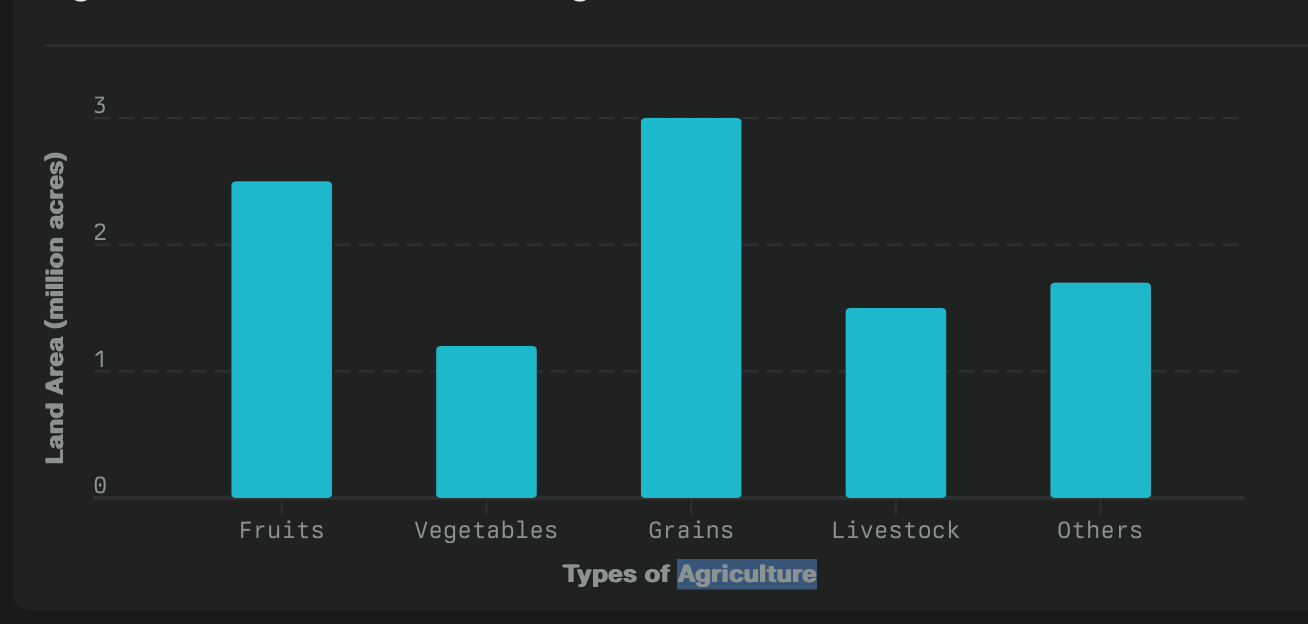
Georgia is a major agricultural state in the U.S., contributing significantly to both the national and state economies. The state's top agricultural commodities are diverse, benefiting from Georgia's favorable climate and large farming areas. Here are the most important agricultural items produced in Georgia:
What are Georgia top 10 agricultural commodities ?
- Broilers (Chickens): Georgia consistently ranks as the top producer of broilers in the U.S., with over 1.31 billion broilers produced in 2022. This commodity is the state's largest agricultural product by value, generating billions annually[1][2][5].
- Peanuts: Georgia leads the nation in peanut production, accounting for nearly half of the U.S. supply. In 2022, the state produced 2.86 billion pounds of peanuts[2][5].
- Cotton: Cotton is another major crop, with Georgia ranking second in the U.S. for cotton lint and seed production. In 2022, the state harvested 2.65 million bales of cotton[2][5].
- Chicken Eggs: Georgia is a top producer of chicken eggs, ranking sixth nationally with over 5.20 billion eggs produced in 2022[5].
- Pecans: The state ranks first in pecan production, with 132 million pounds produced in 2022[2][5].
- Blueberries: Georgia is one of the largest producers of blueberries in the U.S., ranking fourth nationally with nearly 60 million pounds produced in recent years[2][5].
- Timber: Georgia has a vast forestry industry, contributing significantly to its economy through timber production and related products[2][3].
- Cattle and Calves: Beef production is also important, with cattle raised across all counties contributing significantly to agricultural receipts[2][3].
- Greenhouse/Nursery Products: These products, including ornamental plants and turfgrass, are a substantial part of Georgia's agricultural output[1][3].
- Corn: Corn is primarily grown for livestock feed and ethanol production, contributing hundreds of millions to the state's economy[1][3].
Georgia's agriculture is highly diversified, with other notable crops including onions (especially Vidalia onions), watermelons, peaches, and bell peppers[2][4]. This diversity ensures that Georgia remains a key player in both national and international agricultural markets.
The most profitable agricultural products in Georgia are those that contribute the most to the state's economy based on cash receipts. Here are the top agricultural commodities:
1. Broilers (Chickens)
- Value: $6.67 billion (2022)
- Rank: Georgia is the leading producer of broilers in the U.S. This is the state's top agricultural product, contributing significantly to its economy[1][5].
2. Cotton
- Value: $1.26 billion (2022)
- Rank: Georgia ranks second in the U.S. for cotton production, making it one of the state's most valuable crops[1][5].
3. Peanuts
- Value: $960 million (2022)
- Rank: Georgia is the largest peanut producer in the U.S., accounting for over 50% of the nation's peanut production[1][5].
4. Chicken Eggs
- Value: $757 million (2022)
- Rank: Georgia ranks sixth in chicken egg production, contributing significantly to its agricultural revenue[1][5].
5. Pecans
- Value: $213 million (2022)
- Rank: Georgia leads the U.S. in pecan production, making it a key crop for the state[1][5].
6. Corn
- Value: $457 million (2022)
- Corn is primarily grown for livestock feed and ethanol production, and it is another important crop for Georgia's economy[1][5].
7. Greenhouse/Nursery Products
- Value: $376 million (2013)
- Greenhouse and nursery products, including ornamental plants, are a significant part of Georgia's agricultural sector[1].
These commodities form the backbone of Georgia's agriculture industry, contributing billions to the state's economy annually.
How has cotton production evolved in Georgia over the years
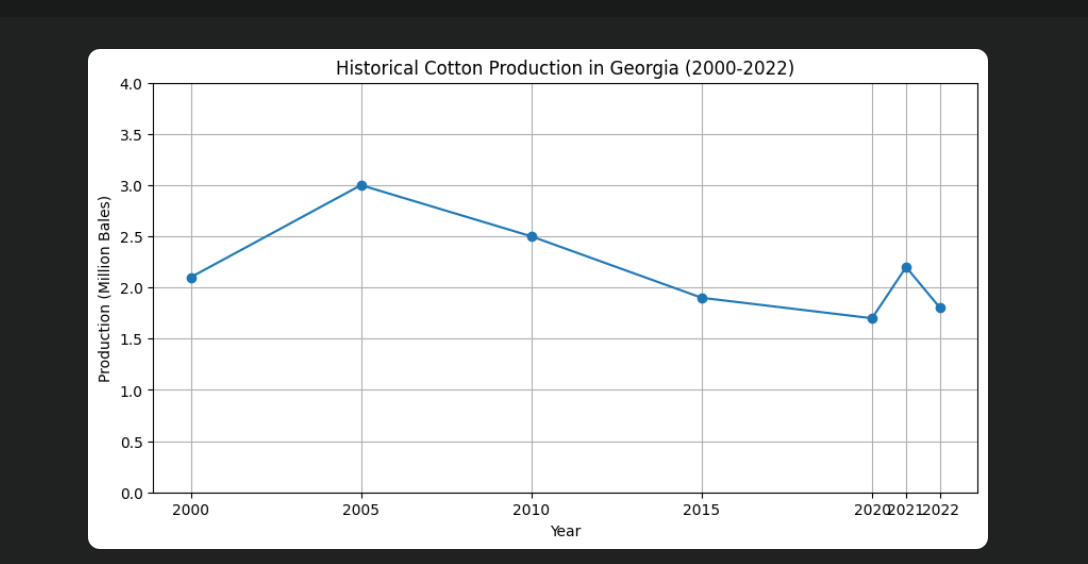
The graph you provided shows the historical cotton production in Georgia from 2000 to 2022. Here's a summary of how cotton production has evolved over the years based on the graph:
Key Trends in Cotton Production in Georgia (2000-2022)
- Early 2000s Growth:
- Cotton production started at around 2.1 million bales in 2000.
- By 2005, production peaked at around 3.0 million bales, indicating a period of strong growth.
- Gradual Decline:
- After 2005, production began to decline, reaching about 2.5 million bales by 2010.
- This decline continued into the mid-2010s, with production dropping to around 1.9 million bales by 2015.
- Recent Fluctuations:
- In 2020, production hit a low of approximately 1.7 million bales, but then rebounded slightly to 2.2 million bales in 2021.
- By 2022, production decreased again to about 1.8 million bales.
Overall Observations
- Cotton production in Georgia has fluctuated over the past two decades, with a peak in the mid-2000s followed by a general downward trend.
- Recent years have seen some recovery, but production remains below the levels seen in the early 2000s.
This trend reflects various factors affecting cotton farming, such as weather conditions, market prices, and changes in agricultural practices or land use.
Citations:
[1] https://farmflavor.com/georgia/georgia-crops-livestock/top-10-commodities-georgia/
[2] https://stacker.com/georgia/most-valuable-crops-grown-georgia
[3] https://agamerica.com/blog/the-land-lenders-talk-top-agriculture-commodities-in-georgia/
[4] https://extension.uga.edu/publications/detail.html?number=AP130-2-02&title=2024-georgia-agriculture-outlook
[5] https://www.nass.usda.gov/Statistics_by_State/Georgia/Publications/More_Features/GAAgFacts2023.pdf